计算器实现原理
要实现一个计算器的功能,通常的思路是:
- 等待用户输入完成,比如输入了
2*(4+2)/6; - 根据输入的内容计算出结果;
使用 eval 函数可以轻易的计算出结果,如果不使用 eval 函数,又该怎么实现呢?
eval(expression);
中缀表达式和后缀表达式
上面的表达式——2*(4+2)/6 被称为中缀表达式,是一个通用的算术或逻辑公式表示方法,操作符处于操作数的中�间,中缀表达式是人们常用的算术表示方法。
但是中缀表达式却不容易被计算机解析。中缀表达式中由于运算符优先级而需要进行中间步骤(比如乘除比加减优先级高,而小括号优先级更高),但计算机更擅长顺序执行;
后缀表达式也称为逆波兰式,逆波兰式对于计算机是比较简单易懂的结构,但对人类的思维结构来说却不容易理解。
2*(4+2)/6 写成逆波兰式则是:242+*6/。
逆波兰式求值过程
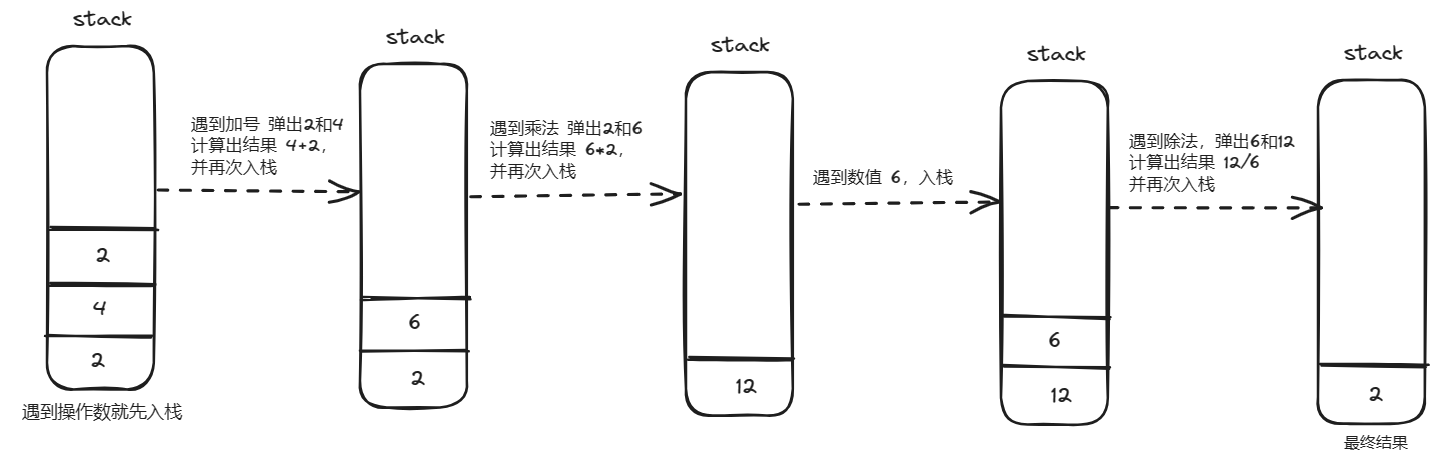
242+*6/ 表达式求值的过程如下:
- 从左到右扫描字符串,把操作数压入栈中;
- 如果遇到操作符,则弹出栈中前两个操作数进行运算;
- 把上一步的运算结果再次压入栈中;
- 重复 2-3 的步骤,直到表达式遍历完,这时候栈里会只剩下一个操作数,这个操作数就是最终的运算结果;
核心代码:
const isNumber = (char: string) => {
const charCode = char.charCodeAt(0);
return charCode > 47 && charCode < 58;
}
function calcReversePolishNotation(expression: string) {
const stack: string[] = [];
/** 遍历表达式 */
for (let char of expression) {
/** 是不是数字,是的话就入栈 */
if (isNumber(char)) {
stack.push(char);
continue;
}
/** 是操作符的情况就计算结果,然后把结果再入栈 */
const newVal = `${calc(char)}`;
/** 把新的值再次压入栈中 */
stack.push(newVal);
}
/** 把最后的计算结果弹出即可 */
return stack.pop();
}
// test: 2*(4+2)/3
const result = calcReversePolishNotation('242+*3/');
console.log(result); // 4
上面代码中,计算 newVal 的主要的流程是:弹出两个栈顶成员,根据操作符做相应运算。代码如下:
const calcMap = {
'+': (num1: number, num2: number) => num1 + num2,
'-': (num1: number, num2: number) => num1 - num2,
'*': (num1: number, num2: number) => num1 * num2,
'/': (num1: number, num2: number) => num1 / num2,
} as const;
const calc = (operator: string): number => {
// 出栈
const num1 = stack.pop();
const num2 = stack.pop();
if (typeof num1 !== 'number' || typeof num2 !== 'number') {
throw new Error('Wrong expression');
}
/** 看操作符是不是符合要求的 */
if (operator in calcMap) {
return calcMap[operator](Number(num2), Number(num1));
}
throw new Error('Unknown expression');
}
中缀表达式转后缀表达式
我们要设计一个计算器程序,用户输入的是更符合人类逻辑思维的中缀表达式,那如何把一个中缀表达式转成后缀表达式呢?
思路
- 初始化两个栈,
operatorStack用于存储运算符,calcResultStack用于存储中间运算结果; - 从左至右扫描中缀表达式;
- 遇到操作数时,将其压入
calcResultStack; - 遇到运算符时,比较它与
operatorStack栈顶运算符的优先级:- 如果
operatorStack为空,或者栈顶运算符为左括号,则直接将它入栈; - 否则,若优先级比栈顶的运算符高,也将其压入
operatorStack; - 否则,将
operatorStack栈顶的运算符弹出并压入calcResultStack中,再把当前的运算符压入到operatorStack中;
- 如果
- 遇到括号时:
- 如果是左括号,则直接压入
operatorStack; - 如果是右括号,则依次弹出
operatorStack栈顶的运算符,并压入calcResultStack,直到遇到左括号为止,此时将这一对括号丢弃;
- 如果是左括号,则直接压入
- 重复步骤 2~5,直到表达式遍历完成,最后把
operatorStack中还剩余的操作符都放入calcResultStack中;
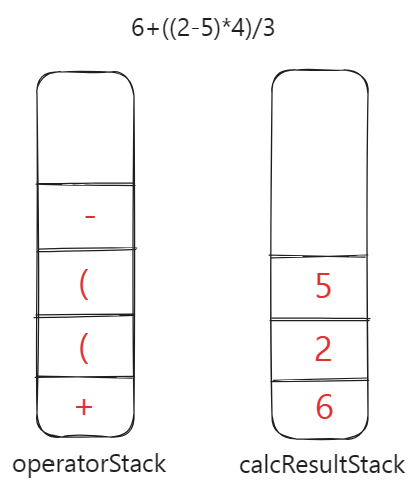
以中缀表达式 6+((2-5)*4)/3 为例(后面以变量exp替代),说明一下步骤。
- 首先第一步,从左往右遍历表达式,遍历到第一个右括号之前都是入栈的操作。
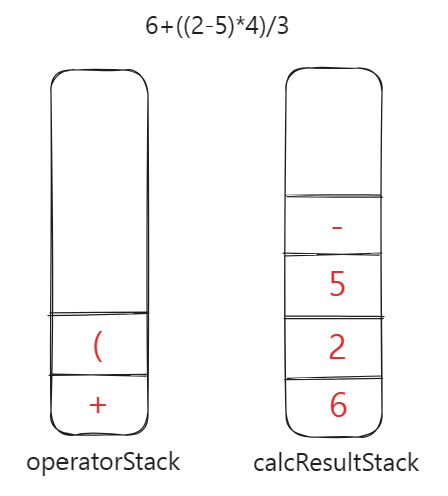
- 遇到第一个右括号,则依次弹出 operatorStack 栈顶的运算符,并压入 calcResultStack 中,直到遇到第一个左括号未知,并把这个左括号从栈中弹出丢弃。
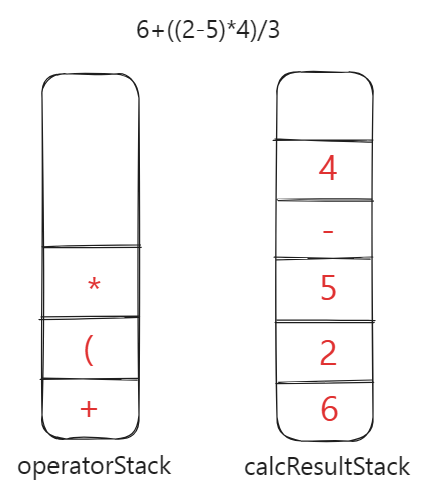
- 接下来还是继续遍历,依次入栈。
- 遇到第二个右括号,重复上面的步骤二。
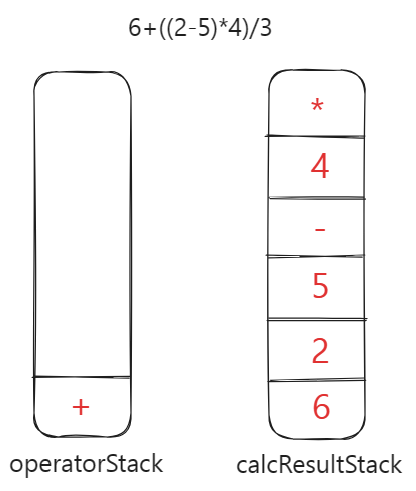
- 遇到
/运算符,它与operatorStack中的栈顶运算符比较,发现优先级比+高,则把/压入operatorStack。然后数字3压入到calcResultStack中。
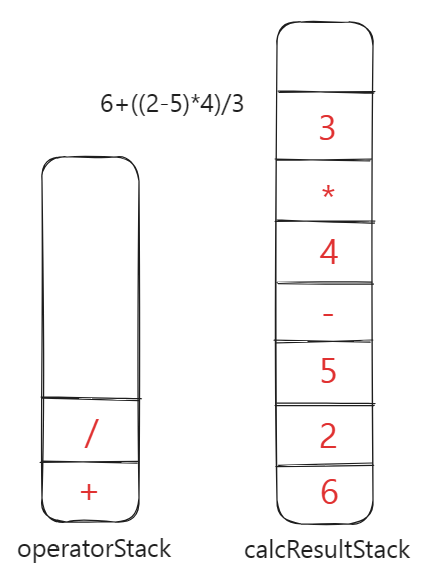
- 表达式扫描完成,把
operatorStack中剩余的操作符压入calcResultStack。
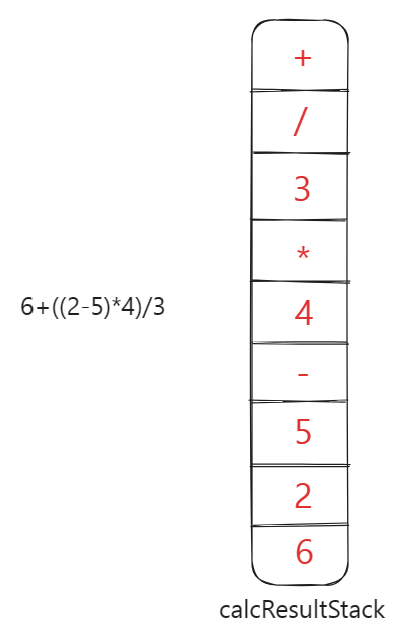
- 从栈底遍历,得到最终的后缀表达式:
625-4*3/+。
实现
首先是一些工具函数,主要包括:
- 存放运算符和中间计算结果的栈;
- 计算函数,用于计算中间值;
- 操作符优先级,用
map表示; - 判断字符是不是运算符、数字、括号、小数点等;
- 判断栈顶元素与新传入的操作符谁的优先级高;
- 判断栈顶元素是不是左括号,扫描表达式遇到右括号时会用到;
- 更新栈顶元素,主要是处理操作数时小数或者多于1位的数字;
class Calculator {
/**
* 用于存储运算符(+、-、*、/ 等)
*/
private operatorStack: string[] = [];
/**
* 用于存储计算时的中间结果
*/
private calcResultStack: (number | string)[] = [];
/** 空格 */
private spaceReg = /\s+/;
/**
* 运算符和优先级,数值越大,优先级越高
*/
private operator = new Map([
['+', 1],
['-', 1],
['*', 2],
['/', 2],
]);
/**
* 计算函数
*/
public calcFn = {
'+': (num1: number, num2: number) => num1 + num2,
'-': (num1: number, num2: number) => num1 - num2,
'*': (num1: number, num2: number) => num1 * num2,
'/': (num1: number, num2: number) => num1 / num2,
} as const;
/**
* 判断传入的字符是不是数字
*
* @param char string
* @returns boolean
*/
public isNumber(char: string) {
const charCode = char.charCodeAt(0);
return charCode > 47 && charCode < 58;
}
/**
* 判断字符是不是运算符
*/
public isOperator(char: string) {
return this.operator.has(char);
}
/**
* 判断字符是不是小数点
*/
public isPoint(char: string) {
return char === '.';
}
/**
* 判断是不是左括号
*/
public isLeftBracket(char: string) {
return char === '(';
}
/**
* 判断是不是右括号
*/
public isRightBracket(char: string) {
return char === ')';
}
/**
* 判断是不是空栈
*/
public isEmptyStack(stack: string[]) {
return stack.length <= 0;
}
/**
* 获取栈顶元素
*/
public getStackTopItem(stack: string[]) {
return stack[stack.length - 1];
}
/** 栈顶元素是不是左括号 */
public stackTopIsLeftBracket(stack: string[]) {
var item = this.getStackTopItem(stack);
return this.isLeftBracket(item);
}
/**
* 判断传入的 operator 是不是比 stack 顶部优先级高
*
* @param stack 操作符栈
* @param operator 操作符
* @returns boolean
*/
public isHigherPriority(stack: string[], operator: string) {
var top = this.getStackTopItem(stack);
return this.getPriority(top) < this.getPriority(operator);
}
/**
* 更新数值栈的栈顶
* 比如遇到小数点,需要把之前的数字拼接上小数点
*
* @param stack 更新数值栈顶
* @param operator string
*/
private updateStackTop(stack: (string | number)[], operator: string) {
let top = stack.pop() ?? "";
top += operator;
stack.push(top);
}
/**
* 获取运算符优先级
*
* @param operator 运算符
* @returns number
*/
public getPriority(operator: string) {
return this.operator.get(operator) || -1;
}
/**
* 计算
*/
private getCalcRes(stack: number[], operator: string) {
const top = stack.pop();
const second = stack.pop();
return this.getResult(second, top, operator);
}
/**
* 计算结果
*/
public getResult(num1: number, num2: number, operator: string): number {
if (operator in this.calcFn) {
return this.calcFn[operator](num1, num2);
}
this.throwErr(`Wrong expression', ${num1} ${operator} ${num2}`);
}
/** 异常 */
private throwErr(error: any = 'Wrong expression'): never {
throw new Error(error);
}
}
转换函数
转换函数内部会遍历中缀表达式,遇到一个字符就需要判断是操作符还是数字或者别的类型,然后做相应的处理。
public transform(expression: string): (string | number)[] {
let prevVal = ''; // 记录前一个字符
const { operatorStack, calcResultStack } = this;
for (let item of expression) {
// 当是空格时,则忽略
if (this.spaceReg.test(item)) continue;
// 是数字
if (this.isNumber(item)) {
// TODO...
}
// 是小数点
else if (this.isPoint(item)) {
// TODO...
}
// 是操作符
else if (this.isOperator(item)) {
// TODO...
}
// 是左括号,直接 push
else if (this.isLeftBracket(item)) {
operatorStack.push(item);
}
// 是右括号
else if (this.isRightBracket(item)) {
// TODO...
}
// 否则认为表达式不正确
else {
return this.throwErr();
}
// 更新前一个值
prevVal = item;
}
// 最后把�剩下的操作符移入 calcResultStack 中
while(operatorStack.length) {
calcResultStack.push(operatorStack.pop());
}
return calcResultStack;
}
上面代码中除了左括号和空格时好处理,其他都需要额外的边界判断,下面一一分析。
首先是数字时,代码如下:
// 是数字
if (this.isNumber(item)) {
// 如果当前是数字,看看上一次的输入是不是也是数字或者小数点,
// 是的话就拼接,否则就直接 push
prevVal && (this.isNumber(prevVal) || this.isPoint(prevVal)) ?
this.updateStackTop(calcResultStack, item) :
calcResultStack.push(Number(item));
}
然后是小数点:
// 是小数点
else if (this.isPoint(item)) {
// 如果当前是小数点,prevVal 是数字,那么就检查栈顶元素是不是已经有了小数点
const top = this.getStackTopItem(calcResultStack);
// 栈顶和当前都是小数点,认为表达式不正确
if (top === '.') return this.throwErr();
// 没有小数点就更新栈顶元素(字符拼接)
this.updateStackTop(calcResultStack, item);
}
然后是操作符:
// 是操作符
else if (this.isOperator(item)) {
// 当前和上一次都是操作符,则认为表达式不正确
if (prevVal && this.isOperator(prevVal)) {
return this.throwErr();
}
while (true) {
// 如果操作符栈是空栈,或者栈顶是左括号,则直接 push
if (this.isEmptyStack(operatorStack) || this.stackTopIsLeftBracket(operatorStack)) {
operatorStack.push(item);
break;
}
// 如果栈顶运算符比当前的运算符优先级低,则直接 push
if (this.isHigherPriority(operatorStack, item)) {
operatorStack.push(item);
break;
}
// 否则,把栈顶元素弹出,然后加入到 calcResultStack
// 循环直到 operatorStack 变成空栈或者顶运算符比 item 优先级高
const top = operatorStack.pop();
calcResultStack.push(top);
}
}
最后是右括号:
// 是右括号,需要弹出 operatorStack 中的操作符
// 直到遇到第一个左括号结束
else if (this.isRightBracket(item)) {
let hasLeftBracket = false;
while (operatorStack.length) {
// 弹出操作符栈栈顶元素
const op = operatorStack.pop();
// 判断是不是左括号,是的话跳出循环
if (this.isLeftBracket(op)) {
hasLeftBracket = true;
break;
}
// 不是左括号,则把运算符 push 到 calcResultStack
calcResultStack.push(op);
}
// 到最后都没有找到左括号,说明表达式有问题
if (!hasLeftBracket) return this.throwErr();
}
transform 函数最后返回的是一个 Array<number|string>,内部可能是操作符、小数数字或者整数。
计算函数
转换成逆波兰式后,接下来就是最终的计算了,代码与上面 逆波兰式求值过程 章节基本一样,代码如下:
public calc(expression: (string | number)[]) {
const stack: number[] = [];
for (let item of expression) {
// 是数字,并且不是 NaN
if (typeof item === 'number' && item === item) {
stack.push(item);
}
// 是字符串类型
else if (typeof item === 'string') {
// 是空白字符,则忽略
if (this.spaceReg.test(item)) continue;
const num = Number(item);
// 是数字字符,直接 push
if (num === num) {
stack.push(num);
continue;
}
// 是操作符
else if (this.isOperator(item)) {
if (stack.length > 1) {
const newVal = this.getCalcRes(stack, item);
stack.push(newVal);
}
// 如果 stack 中没有两个数值,表明这个表达式不合法
else return this.throwErr();
}
} else {
return this.throwErr();
}
}
// 返回最终结果
return stack[0];
}
到此,一个简单的计算器就实现了,简单测试一把:
// test-1: 支持小数
let exp = '1.8+((2-3.5)*4)-5.8';
let calcu = new Calculator();
let rs = calcu.transform(exp);
console.log('rs-1 ===>', rs);
console.log('result-1 ===>', calcu.calc(rs)); // -10
// test-2
exp = '6*((13-5)/4)+3';
calcu = new Calculator();
rs = calcu.transform(exp);
console.log('rs-2 ===>', rs);
console.log('result-2 ===>', calcu.calc(rs)); // 15
前缀表达式
除了中缀表达式和后缀表达式外,还有前缀表达式,前缀表达式的操作符通常都在数字的前面。
前缀表达式求值过程如下:
- 从右至左遍历前缀表达式;
- 遇到数字压入堆栈;
- 遇到运算符时,弹出栈顶两个数,用运算符做相应的运算(栈顶元素和次顶元素),并将结果入栈;
- 重复上面操作过程,直到遍历完表达式;
比如 (3+4)*5-6 对应的前缀表达式为 -*+3456,求值过程就不演示了,大家可以按照上面步骤演算一下。